This tutorial will cover how to implement shadow mapping in DirectX 11 using C++ and HLSL.
Before proceeding with this tutorial, you should first have a clear understanding of the following concepts: Render to Texture (Tutorial 25), Depth Buffers (Tutorial 35), and Projective Texturing (Tutorial 39).
Shadow mapping is one of the fastest and CPU/GPU efficient methods for rendering shadows in small to medium sized scenes.
It is also one of the simpler methods that gives highly realistic results.
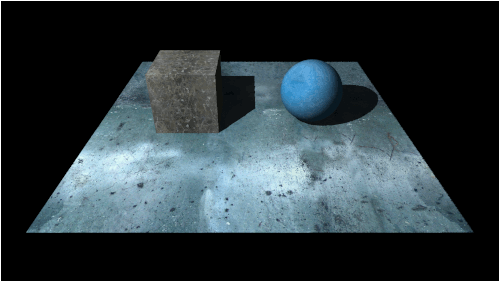
To understand how shadow mapping works we will start with a basic scene that is illuminated with a single point light:
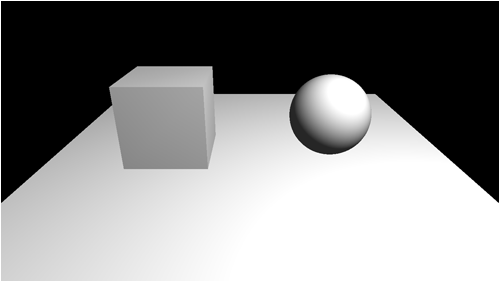
The light that is illuminating the scene is originating from behind and to the right of our current camera position.
The light position is very important as the next step is that we will render the scene from the point of view of the light.
When we render from the light's point of view we will render just the depth buffer information into a render to texture.
This render to texture filled with depth information is called the Shadow Map and looks like the following:
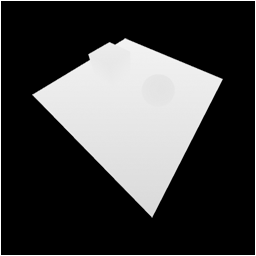
Now that we have the depth information of all the objects in the scene that could possibly cast a shadow we can now figure out where the shadows should occur.
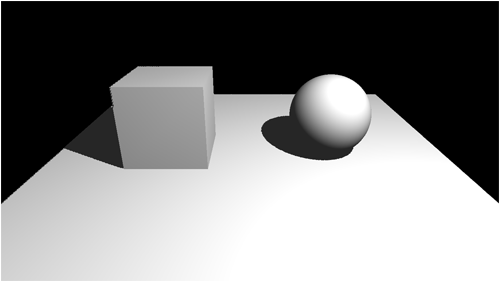
When we render the scene, we will project the shadow map texture back onto the scene to get the depth of any objects that cast shadows and compare it with the position of the light on a per pixel basis in the pixel shader.
If we find the light is closer to the camera then we light the pixel.
If we find the object is closer to the camera then we shadow the pixel.
Doing so produces the following image:
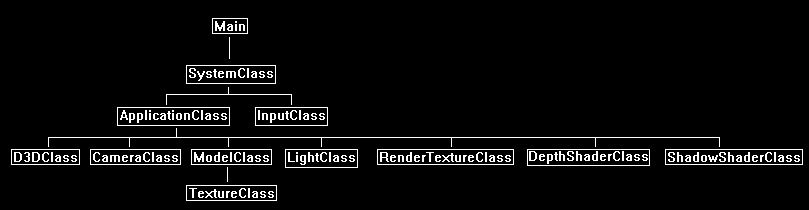
Framework
The framework is similar to the last tutorial, except that we will now need RenderTextureClass and DepthShaderClass from the previous tutorials.
And we will also need a new class named ShadowShaderClass.
We will start the code section of the shadow map tutorial by examining the HLSL shaders first.
The shadow shader is based mostly on the projection shader from the previous tutorial.
Shadow.vs
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: shadow.vs
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/////////////
// GLOBALS //
/////////////
The second view and projection matrices have been renamed to lightViewMatrix and lightProjectionMatrix.
cbuffer MatrixBuffer
{
matrix worldMatrix;
matrix viewMatrix;
matrix projectionMatrix;
matrix lightViewMatrix;
matrix lightProjectionMatrix;
};
cbuffer LightPositionBuffer
{
float3 lightPosition;
float padding;
};
//////////////
// TYPEDEFS //
//////////////
struct VertexInputType
{
float4 position : POSITION;
float2 tex : TEXCOORD0;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
};
The view position output has also been renamed to lightViewPosition.
struct PixelInputType
{
float4 position : SV_POSITION;
float2 tex : TEXCOORD0;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
float4 lightViewPosition : TEXCOORD1;
float3 lightPos : TEXCOORD2;
};
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Vertex Shader
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
PixelInputType ShadowVertexShader(VertexInputType input)
{
PixelInputType output;
float4 worldPosition;
// Change the position vector to be 4 units for proper matrix calculations.
input.position.w = 1.0f;
// Calculate the position of the vertex against the world, view, and projection matrices.
output.position = mul(input.position, worldMatrix);
output.position = mul(output.position, viewMatrix);
output.position = mul(output.position, projectionMatrix);
The output light view position has had the variables renamed to correctly reflect what data they represent.
// Calculate the position of the vertice as viewed by the light source.
output.lightViewPosition = mul(input.position, worldMatrix);
output.lightViewPosition = mul(output.lightViewPosition, lightViewMatrix);
output.lightViewPosition = mul(output.lightViewPosition, lightProjectionMatrix);
// Store the texture coordinates for the pixel shader.
output.tex = input.tex;
// Calculate the normal vector against the world matrix only.
output.normal = mul(input.normal, (float3x3)worldMatrix);
// Normalize the normal vector.
output.normal = normalize(output.normal);
// Calculate the position of the vertex in the world.
worldPosition = mul(input.position, worldMatrix);
// Determine the light position based on the position of the light and the position of the vertex in the world.
output.lightPos = lightPosition.xyz - worldPosition.xyz;
// Normalize the light position vector.
output.lightPos = normalize(output.lightPos);
return output;
}
Shadow.ps
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: shadow.ps
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/////////////
// GLOBALS //
/////////////
Texture2D shaderTexture : register(t0);
The depthMapTexture is the shadow map.
This texture contains the scene depth buffer rendered from the light's perspective.
Texture2D depthMapTexture : register(t1);
We require a clamp-based sampler when sampling the depth buffer so that it doesn't wrap around and sample incorrect information.
And we also require a wrap sampler for rendering objects such as the sphere that has that type of texture mapping.
SamplerState SampleTypeClamp : register(s0);
SamplerState SampleTypeWrap : register(s1);
//////////////
// TYPEDEFS //
//////////////
struct PixelInputType
{
float4 position : SV_POSITION;
float2 tex : TEXCOORD0;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
float4 lightViewPosition : TEXCOORD1;
float3 lightPos : TEXCOORD2;
};
//////////////////////
// CONSTANT BUFFERS //
//////////////////////
cbuffer LightBuffer
{
float4 ambientColor;
float4 diffuseColor;
float bias;
float3 padding;
};
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Pixel Shader
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
float4 ShadowPixelShader(PixelInputType input) : SV_TARGET
{
float4 color;
float2 projectTexCoord;
float depthValue;
float lightDepthValue;
float lightIntensity;
float4 textureColor;
// Set the default output color to the ambient light value for all pixels.
color = ambientColor;
Calculate the projected texture coordinates for sampling the shadow map (depth buffer texture) based on the light's viewing position.
// Calculate the projected texture coordinates.
projectTexCoord.x = input.lightViewPosition.x / input.lightViewPosition.w / 2.0f + 0.5f;
projectTexCoord.y = -input.lightViewPosition.y / input.lightViewPosition.w / 2.0f + 0.5f;
Check if the projected coordinates are in the view of the light, if not then the pixel gets just an ambient value.
// Determine if the projected coordinates are in the 0 to 1 range. If it is then this pixel is inside the projected view port.
if((saturate(projectTexCoord.x) == projectTexCoord.x) && (saturate(projectTexCoord.y) == projectTexCoord.y))
{
Now that we are in the view of the light, we will retrieve the depth value from the shadow map (depthMapTexture).
We only sample the red component since this is a grey scale texture.
The depth value we get from the texture translates into the distance to the nearest object.
This is important since objects are what cast the shadows and hence why it is called a shadow map.
// Sample the shadow map depth value from the depth texture using the sampler at the projected texture coordinate location.
depthValue = depthMapTexture.Sample(SampleTypeClamp, projectTexCoord).r;
Now that we have the depth of the object for this pixel, we need the depth of the light to determine if it is in front or behind the object.
We get this from the lightViewPosition.
Note that we need to subtract the bias from this or we will get the floating-point precision issue.
// Calculate the depth of the light.
lightDepthValue = input.lightViewPosition.z / input.lightViewPosition.w;
// Subtract the bias from the lightDepthValue.
lightDepthValue = lightDepthValue - bias;
Now we perform the comparison between the light depth and the object depth.
If the light is closer to us then no shadow.
But if the light is behind an object in the shadow map, then it gets shadowed.
Note that a shadow just means we only use the default ambient light, we don't color it black or anything.
// Compare the depth of the shadow map value and the depth of the light to determine whether to shadow or to light this pixel.
// If the light is in front of the object then light the pixel, if not then shadow this pixel since an object (occluder) is casting a shadow on it.
if(lightDepthValue < depthValue)
{
// Calculate the amount of light on this pixel.
lightIntensity = saturate(dot(input.normal, input.lightPos));
if(lightIntensity > 0.0f)
{
If the light was in front of the object, then there is no shadow and we do regular lighting.
// Determine the final diffuse color based on the diffuse color and the amount of light intensity.
color += (diffuseColor * lightIntensity);
// Saturate the final light color.
color = saturate(color);
}
}
}
// Sample the pixel color from the texture using the sampler at this texture coordinate location.
textureColor = shaderTexture.Sample(SampleTypeWrap, input.tex);
// Combine the light and texture color.
color = color * textureColor;
return color;
}
Shadowshaderclass.h
The ShadowShaderClass is just the ProjectionShaderClass modified for shadows.
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: shadowshaderclass.h
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#ifndef _SHADOWSHADERCLASS_H_
#define _SHADOWSHADERCLASS_H_
//////////////
// INCLUDES //
//////////////
#include <d3d11.h>
#include <d3dcompiler.h>
#include <directxmath.h>
#include <fstream>
using namespace DirectX;
using namespace std;
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Class name: ShadowShaderClass
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class ShadowShaderClass
{
private:
The MatrixBufferType has had the second view and projection matrices renamed.
struct MatrixBufferType
{
XMMATRIX world;
XMMATRIX view;
XMMATRIX projection;
XMMATRIX lightView;
XMMATRIX lightProjection;
};
struct LightPositionBufferType
{
XMFLOAT3 lightPosition;
float padding;
};
The LightBufferType now contains a bias for controlling the slight offset of the light depth sampling.
struct LightBufferType
{
XMFLOAT4 ambientColor;
XMFLOAT4 diffuseColor;
float bias;
XMFLOAT3 padding;
};
public:
ShadowShaderClass();
ShadowShaderClass(const ShadowShaderClass&);
~ShadowShaderClass();
bool Initialize(ID3D11Device*, HWND);
void Shutdown();
bool Render(ID3D11DeviceContext*, int, XMMATRIX, XMMATRIX, XMMATRIX, XMMATRIX, XMMATRIX, ID3D11ShaderResourceView*, ID3D11ShaderResourceView*,
XMFLOAT4, XMFLOAT4, XMFLOAT3, float);
private:
bool InitializeShader(ID3D11Device*, HWND, WCHAR*, WCHAR*);
void ShutdownShader();
void OutputShaderErrorMessage(ID3D10Blob*, HWND, WCHAR*);
bool SetShaderParameters(ID3D11DeviceContext*, XMMATRIX, XMMATRIX, XMMATRIX, XMMATRIX, XMMATRIX, ID3D11ShaderResourceView*, ID3D11ShaderResourceView*,
XMFLOAT4, XMFLOAT4, XMFLOAT3, float);
void RenderShader(ID3D11DeviceContext*, int);
private:
ID3D11VertexShader* m_vertexShader;
ID3D11PixelShader* m_pixelShader;
ID3D11InputLayout* m_layout;
ID3D11Buffer* m_matrixBuffer;
We will require a clamp and a wrap sampler type.
ID3D11SamplerState* m_sampleStateClamp;
ID3D11SamplerState* m_sampleStateWrap;
ID3D11Buffer* m_lightPositionBuffer;
ID3D11Buffer* m_lightBuffer;
};
#endif
Shadowshaderclass.cpp
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: shadowshaderclass.cpp
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#include "shadowshaderclass.h"
ShadowShaderClass::ShadowShaderClass()
{
m_vertexShader = 0;
m_pixelShader = 0;
m_layout = 0;
m_matrixBuffer = 0;
m_sampleStateClamp = 0;
m_sampleStateWrap = 0;
m_lightPositionBuffer = 0;
m_lightBuffer = 0;
}
ShadowShaderClass::ShadowShaderClass(const ShadowShaderClass& other)
{
}
ShadowShaderClass::~ShadowShaderClass()
{
}
bool ShadowShaderClass::Initialize(ID3D11Device* device, HWND hwnd)
{
wchar_t vsFilename[128], psFilename[128];
int error;
bool result;
We load the shadow.vs and shadow.ps HLSL shader files here.
// Set the filename of the vertex shader.
error = wcscpy_s(vsFilename, 128, L"../Engine/shadow.vs");
if(error != 0)
{
return false;
}
// Set the filename of the pixel shader.
error = wcscpy_s(psFilename, 128, L"../Engine/shadow.ps");
if(error != 0)
{
return false;
}
// Initialize the vertex and pixel shaders.
result = InitializeShader(device, hwnd, vsFilename, psFilename);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
void ShadowShaderClass::Shutdown()
{
// Shutdown the vertex and pixel shaders as well as the related objects.
ShutdownShader();
return;
}
The render function will send in all the new variables to be set in the shadow vertex and pixel shaders.
bool ShadowShaderClass::Render(ID3D11DeviceContext* deviceContext, int indexCount, XMMATRIX worldMatrix, XMMATRIX viewMatrix, XMMATRIX projectionMatrix,
XMMATRIX lightViewMatrix, XMMATRIX lightProjectionMatrix, ID3D11ShaderResourceView* texture, ID3D11ShaderResourceView* depthMapTexture,
XMFLOAT4 ambientColor, XMFLOAT4 diffuseColor, XMFLOAT3 lightPosition, float bias)
{
bool result;
// Set the shader parameters that it will use for rendering.
result = SetShaderParameters(deviceContext, worldMatrix, viewMatrix, projectionMatrix, lightViewMatrix, lightProjectionMatrix, texture, depthMapTexture,
ambientColor, diffuseColor, lightPosition, bias);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
// Now render the prepared buffers with the shader.
RenderShader(deviceContext, indexCount);
return true;
}
bool ShadowShaderClass::InitializeShader(ID3D11Device* device, HWND hwnd, WCHAR* vsFilename, WCHAR* psFilename)
{
HRESULT result;
ID3D10Blob* errorMessage;
ID3D10Blob* vertexShaderBuffer;
ID3D10Blob* pixelShaderBuffer;
D3D11_INPUT_ELEMENT_DESC polygonLayout[3];
unsigned int numElements;
D3D11_BUFFER_DESC matrixBufferDesc;
D3D11_SAMPLER_DESC samplerDesc;
D3D11_BUFFER_DESC lightBufferDesc;
D3D11_BUFFER_DESC lightPositionBufferDesc;
// Initialize the pointers this function will use to null.
errorMessage = 0;
vertexShaderBuffer = 0;
pixelShaderBuffer = 0;
Load the shadow vertex shader.
// Compile the vertex shader code.
result = D3DCompileFromFile(vsFilename, NULL, NULL, "ShadowVertexShader", "vs_5_0", D3D10_SHADER_ENABLE_STRICTNESS, 0,
&vertexShaderBuffer, &errorMessage);
if(FAILED(result))
{
// If the shader failed to compile it should have writen something to the error message.
if(errorMessage)
{
OutputShaderErrorMessage(errorMessage, hwnd, vsFilename);
}
// If there was nothing in the error message then it simply could not find the shader file itself.
else
{
MessageBox(hwnd, vsFilename, L"Missing Shader File", MB_OK);
}
return false;
}
Load the shadow pixel shader.
// Compile the pixel shader code.
result = D3DCompileFromFile(psFilename, NULL, NULL, "ShadowPixelShader", "ps_5_0", D3D10_SHADER_ENABLE_STRICTNESS, 0,
&pixelShaderBuffer, &errorMessage);
if(FAILED(result))
{
// If the shader failed to compile it should have writen something to the error message.
if(errorMessage)
{
OutputShaderErrorMessage(errorMessage, hwnd, psFilename);
}
// If there was nothing in the error message then it simply could not find the file itself.
else
{
MessageBox(hwnd, psFilename, L"Missing Shader File", MB_OK);
}
return false;
}
// Create the vertex shader from the buffer.
result = device->CreateVertexShader(vertexShaderBuffer->GetBufferPointer(), vertexShaderBuffer->GetBufferSize(), NULL, &m_vertexShader);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
// Create the pixel shader from the buffer.
result = device->CreatePixelShader(pixelShaderBuffer->GetBufferPointer(), pixelShaderBuffer->GetBufferSize(), NULL, &m_pixelShader);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
// Create the vertex input layout description.
polygonLayout[0].SemanticName = "POSITION";
polygonLayout[0].SemanticIndex = 0;
polygonLayout[0].Format = DXGI_FORMAT_R32G32B32_FLOAT;
polygonLayout[0].InputSlot = 0;
polygonLayout[0].AlignedByteOffset = 0;
polygonLayout[0].InputSlotClass = D3D11_INPUT_PER_VERTEX_DATA;
polygonLayout[0].InstanceDataStepRate = 0;
polygonLayout[1].SemanticName = "TEXCOORD";
polygonLayout[1].SemanticIndex = 0;
polygonLayout[1].Format = DXGI_FORMAT_R32G32_FLOAT;
polygonLayout[1].InputSlot = 0;
polygonLayout[1].AlignedByteOffset = D3D11_APPEND_ALIGNED_ELEMENT;
polygonLayout[1].InputSlotClass = D3D11_INPUT_PER_VERTEX_DATA;
polygonLayout[1].InstanceDataStepRate = 0;
polygonLayout[2].SemanticName = "NORMAL";
polygonLayout[2].SemanticIndex = 0;
polygonLayout[2].Format = DXGI_FORMAT_R32G32B32_FLOAT;
polygonLayout[2].InputSlot = 0;
polygonLayout[2].AlignedByteOffset = D3D11_APPEND_ALIGNED_ELEMENT;
polygonLayout[2].InputSlotClass = D3D11_INPUT_PER_VERTEX_DATA;
polygonLayout[2].InstanceDataStepRate = 0;
// Get a count of the elements in the layout.
numElements = sizeof(polygonLayout) / sizeof(polygonLayout[0]);
// Create the vertex input layout.
result = device->CreateInputLayout(polygonLayout, numElements, vertexShaderBuffer->GetBufferPointer(), vertexShaderBuffer->GetBufferSize(), &m_layout);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
// Release the vertex shader buffer and pixel shader buffer since they are no longer needed.
vertexShaderBuffer->Release();
vertexShaderBuffer = 0;
pixelShaderBuffer->Release();
pixelShaderBuffer = 0;
// Setup the description of the dynamic matrix constant buffer that is in the vertex shader.
matrixBufferDesc.Usage = D3D11_USAGE_DYNAMIC;
matrixBufferDesc.ByteWidth = sizeof(MatrixBufferType);
matrixBufferDesc.BindFlags = D3D11_BIND_CONSTANT_BUFFER;
matrixBufferDesc.CPUAccessFlags = D3D11_CPU_ACCESS_WRITE;
matrixBufferDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
matrixBufferDesc.StructureByteStride = 0;
// Create the constant buffer pointer so we can access the vertex shader constant buffer from within this class.
result = device->CreateBuffer(&matrixBufferDesc, NULL, &m_matrixBuffer);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
Setup both the clamp and the wrap samplers here for the pixel shader to use.
// Create a clamp texture sampler state description.
samplerDesc.Filter = D3D11_FILTER_MIN_MAG_MIP_LINEAR;
samplerDesc.AddressU = D3D11_TEXTURE_ADDRESS_CLAMP;
samplerDesc.AddressV = D3D11_TEXTURE_ADDRESS_CLAMP;
samplerDesc.AddressW = D3D11_TEXTURE_ADDRESS_CLAMP;
samplerDesc.MipLODBias = 0.0f;
samplerDesc.MaxAnisotropy = 1;
samplerDesc.ComparisonFunc = D3D11_COMPARISON_ALWAYS;
samplerDesc.BorderColor[0] = 0;
samplerDesc.BorderColor[1] = 0;
samplerDesc.BorderColor[2] = 0;
samplerDesc.BorderColor[3] = 0;
samplerDesc.MinLOD = 0;
samplerDesc.MaxLOD = D3D11_FLOAT32_MAX;
// Create the clamp texture sampler state.
result = device->CreateSamplerState(&samplerDesc, &m_sampleStateClamp);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
// Create a wrap texture sampler state description.
samplerDesc.Filter = D3D11_FILTER_MIN_MAG_MIP_LINEAR;
samplerDesc.AddressU = D3D11_TEXTURE_ADDRESS_WRAP;
samplerDesc.AddressV = D3D11_TEXTURE_ADDRESS_WRAP;
samplerDesc.AddressW = D3D11_TEXTURE_ADDRESS_WRAP;
samplerDesc.MipLODBias = 0.0f;
samplerDesc.MaxAnisotropy = 1;
samplerDesc.ComparisonFunc = D3D11_COMPARISON_ALWAYS;
samplerDesc.BorderColor[0] = 0;
samplerDesc.BorderColor[1] = 0;
samplerDesc.BorderColor[2] = 0;
samplerDesc.BorderColor[3] = 0;
samplerDesc.MinLOD = 0;
samplerDesc.MaxLOD = D3D11_FLOAT32_MAX;
// Create the wrap texture sampler state.
result = device->CreateSamplerState(&samplerDesc, &m_sampleStateWrap);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
// Setup the description of the light position dynamic constant buffer that is in the vertex shader.
lightPositionBufferDesc.Usage = D3D11_USAGE_DYNAMIC;
lightPositionBufferDesc.ByteWidth = sizeof(LightPositionBufferType);
lightPositionBufferDesc.BindFlags = D3D11_BIND_CONSTANT_BUFFER;
lightPositionBufferDesc.CPUAccessFlags = D3D11_CPU_ACCESS_WRITE;
lightPositionBufferDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
lightPositionBufferDesc.StructureByteStride = 0;
// Create the constant buffer pointer so we can access the vertex shader constant buffer from within this class.
result = device->CreateBuffer(&lightPositionBufferDesc, NULL, &m_lightPositionBuffer);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
// Setup the description of the light dynamic constant buffer that is in the pixel shader.
lightBufferDesc.Usage = D3D11_USAGE_DYNAMIC;
lightBufferDesc.ByteWidth = sizeof(LightBufferType);
lightBufferDesc.BindFlags = D3D11_BIND_CONSTANT_BUFFER;
lightBufferDesc.CPUAccessFlags = D3D11_CPU_ACCESS_WRITE;
lightBufferDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
lightBufferDesc.StructureByteStride = 0;
// Create the constant buffer pointer so we can access the pixel shader constant buffer from within this class.
result = device->CreateBuffer(&lightBufferDesc, NULL, &m_lightBuffer);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
void ShadowShaderClass::ShutdownShader()
{
// Release the light constant buffer.
if(m_lightBuffer)
{
m_lightBuffer->Release();
m_lightBuffer = 0;
}
// Release the light position constant buffer.
if(m_lightPositionBuffer)
{
m_lightPositionBuffer->Release();
m_lightPositionBuffer = 0;
}
// Release the wrap sampler state.
if(m_sampleStateWrap)
{
m_sampleStateWrap->Release();
m_sampleStateWrap = 0;
}
// Release the clamp sampler state.
if(m_sampleStateClamp)
{
m_sampleStateClamp->Release();
m_sampleStateClamp = 0;
}
// Release the matrix constant buffer.
if(m_matrixBuffer)
{
m_matrixBuffer->Release();
m_matrixBuffer = 0;
}
// Release the layout.
if(m_layout)
{
m_layout->Release();
m_layout = 0;
}
// Release the pixel shader.
if(m_pixelShader)
{
m_pixelShader->Release();
m_pixelShader = 0;
}
// Release the vertex shader.
if(m_vertexShader)
{
m_vertexShader->Release();
m_vertexShader = 0;
}
return;
}
void ShadowShaderClass::OutputShaderErrorMessage(ID3D10Blob* errorMessage, HWND hwnd, WCHAR* shaderFilename)
{
char* compileErrors;
unsigned long long bufferSize, i;
ofstream fout;
// Get a pointer to the error message text buffer.
compileErrors = (char*)(errorMessage->GetBufferPointer());
// Get the length of the message.
bufferSize = errorMessage->GetBufferSize();
// Open a file to write the error message to.
fout.open("shader-error.txt");
// Write out the error message.
for(i=0; i<bufferSize; i++)
{
fout << compileErrors[i];
}
// Close the file.
fout.close();
// Release the error message.
errorMessage->Release();
errorMessage = 0;
// Pop a message up on the screen to notify the user to check the text file for compile errors.
MessageBox(hwnd, L"Error compiling shader. Check shader-error.txt for message.", shaderFilename, MB_OK);
return;
}
bool ShadowShaderClass::SetShaderParameters(ID3D11DeviceContext* deviceContext, XMMATRIX worldMatrix, XMMATRIX viewMatrix, XMMATRIX projectionMatrix,
XMMATRIX lightViewMatrix, XMMATRIX lightProjectionMatrix, ID3D11ShaderResourceView* texture, ID3D11ShaderResourceView* depthMapTexture,
XMFLOAT4 ambientColor, XMFLOAT4 diffuseColor, XMFLOAT3 lightPosition, float bias)
{
HRESULT result;
D3D11_MAPPED_SUBRESOURCE mappedResource;
MatrixBufferType* dataPtr;
unsigned int bufferNumber;
LightPositionBufferType* dataPtr2;
LightBufferType* dataPtr3;
The second view and projection matrices are all renamed to lightViewMatrix and lightProjectionMatrix in this function.
// Transpose the matrices to prepare them for the shader.
worldMatrix = XMMatrixTranspose(worldMatrix);
viewMatrix = XMMatrixTranspose(viewMatrix);
projectionMatrix = XMMatrixTranspose(projectionMatrix);
lightViewMatrix = XMMatrixTranspose(lightViewMatrix);
lightProjectionMatrix = XMMatrixTranspose(lightProjectionMatrix);
// Lock the constant buffer so it can be written to.
result = deviceContext->Map(m_matrixBuffer, 0, D3D11_MAP_WRITE_DISCARD, 0, &mappedResource);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
// Get a pointer to the data in the constant buffer.
dataPtr = (MatrixBufferType*)mappedResource.pData;
// Copy the matrices into the constant buffer.
dataPtr->world = worldMatrix;
dataPtr->view = viewMatrix;
dataPtr->projection = projectionMatrix;
dataPtr->lightView = lightViewMatrix;
dataPtr->lightProjection = lightProjectionMatrix;
// Unlock the constant buffer.
deviceContext->Unmap(m_matrixBuffer, 0);
// Set the position of the constant buffer in the vertex shader.
bufferNumber = 0;
// Finally set the constant buffer in the vertex shader with the updated values.
deviceContext->VSSetConstantBuffers(bufferNumber, 1, &m_matrixBuffer);
// Lock the light position constant buffer so it can be written to.
result = deviceContext->Map(m_lightPositionBuffer, 0, D3D11_MAP_WRITE_DISCARD, 0, &mappedResource);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
// Get a pointer to the data in the constant buffer.
dataPtr2 = (LightPositionBufferType*)mappedResource.pData;
// Copy the lighting variables into the constant buffer.
dataPtr2->lightPosition = lightPosition;
dataPtr2->padding = 0.0f;
// Unlock the constant buffer.
deviceContext->Unmap(m_lightPositionBuffer, 0);
// Set the position of the light constant buffer in the vertex shader.
bufferNumber = 1;
// Finally set the light constant buffer in the vertex shader with the updated values.
deviceContext->VSSetConstantBuffers(bufferNumber, 1, &m_lightPositionBuffer);
// Lock the light constant buffer so it can be written to.
result = deviceContext->Map(m_lightBuffer, 0, D3D11_MAP_WRITE_DISCARD, 0, &mappedResource);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
// Get a pointer to the data in the constant buffer.
dataPtr3 = (LightBufferType*)mappedResource.pData;
We are now additionally setting the bias in the m_lightBuffer.
We set the bias here dynamically as this may need to be tweaked heavily and sometimes changed between frames to different values for different scenes.
// Copy the lighting variables into the constant buffer.
dataPtr3->ambientColor = ambientColor;
dataPtr3->diffuseColor = diffuseColor;
dataPtr3->bias = bias;
dataPtr3->padding = XMFLOAT3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
// Unlock the constant buffer.
deviceContext->Unmap(m_lightBuffer, 0);
// Set the position of the light constant buffer in the pixel shader.
bufferNumber = 0;
// Finally set the light constant buffer in the pixel shader with the updated values.
deviceContext->PSSetConstantBuffers(bufferNumber, 1, &m_lightBuffer);
// Set shader texture resources in the pixel shader.
deviceContext->PSSetShaderResources(0, 1, &texture);
deviceContext->PSSetShaderResources(1, 1, &depthMapTexture);
return true;
}
void ShadowShaderClass::RenderShader(ID3D11DeviceContext* deviceContext, int indexCount)
{
// Set the vertex input layout.
deviceContext->IASetInputLayout(m_layout);
// Set the vertex and pixel shaders that will be used to render this triangle.
deviceContext->VSSetShader(m_vertexShader, NULL, 0);
deviceContext->PSSetShader(m_pixelShader, NULL, 0);
Both the clamp and wrap sampler states are set in the pixel shader here.
// Set the sampler state in the pixel shader.
deviceContext->PSSetSamplers(0, 1, &m_sampleStateClamp);
deviceContext->PSSetSamplers(1, 1, &m_sampleStateWrap);
// Render the geometry.
deviceContext->DrawIndexed(indexCount, 0, 0);
return;
}
Depth.ps
For the depth shader we need to modify just the pixel shader so that it returns just the depth as output.
The previous tutorial we had it outputting a range of colors, which is not it's actual purpose.
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: depth.ps
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//////////////
// TYPEDEFS //
//////////////
struct PixelInputType
{
float4 position : SV_POSITION;
float4 depthPosition : TEXTURE0;
};
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Pixel Shader
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
float4 DepthPixelShader(PixelInputType input) : SV_TARGET
{
float depthValue;
float4 color;
// Get the depth value of the pixel by dividing the Z pixel depth by the homogeneous W coordinate.
depthValue = input.depthPosition.z / input.depthPosition.w;
color = float4(depthValue, depthValue, depthValue, 1.0f);
return color;
}
Lightclass.h
The LightClass was modified for this tutorial so that lights can have their own view and projection matrices associated with them.
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: lightclass.h
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#ifndef _LIGHTCLASS_H_
#define _LIGHTCLASS_H_
//////////////
// INCLUDES //
//////////////
#include <directxmath.h>
using namespace DirectX;
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Class name: LightClass
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class LightClass
{
public:
LightClass();
LightClass(const LightClass&);
~LightClass();
void SetAmbientColor(float, float, float, float);
void SetDiffuseColor(float, float, float, float);
void SetDirection(float, float, float);
void SetPosition(float, float, float);
void SetLookAt(float, float, float);
XMFLOAT4 GetAmbientColor();
XMFLOAT4 GetDiffuseColor();
XMFLOAT3 GetDirection();
XMFLOAT3 GetPosition();
void GenerateViewMatrix();
void GenerateProjectionMatrix(float, float);
void GetViewMatrix(XMMATRIX&);
void GetProjectionMatrix(XMMATRIX&);
private:
XMFLOAT4 m_ambientColor;
XMFLOAT4 m_diffuseColor;
XMFLOAT3 m_direction;
XMFLOAT3 m_position;
XMFLOAT3 m_lookAt;
XMMATRIX m_viewMatrix;
XMMATRIX m_projectionMatrix;
};
#endif
Lightclass.cpp
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: lightclass.cpp
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#include "lightclass.h"
LightClass::LightClass()
{
}
LightClass::LightClass(const LightClass& other)
{
}
LightClass::~LightClass()
{
}
void LightClass::SetAmbientColor(float red, float green, float blue, float alpha)
{
m_ambientColor = XMFLOAT4(red, green, blue, alpha);
return;
}
void LightClass::SetDiffuseColor(float red, float green, float blue, float alpha)
{
m_diffuseColor = XMFLOAT4(red, green, blue, alpha);
return;
}
void LightClass::SetDirection(float x, float y, float z)
{
m_direction = XMFLOAT3(x, y, z);
return;
}
void LightClass::SetPosition(float x, float y, float z)
{
m_position = XMFLOAT3(x, y, z);
return;
}
The SetLookAt function sets the m_lookAt vector so that we can set where the light is looking at.
This vector is used to build the light's view matrix.
void LightClass::SetLookAt(float x, float y, float z)
{
m_lookAt = XMFLOAT3(x, y, z);
return;
}
XMFLOAT4 LightClass::GetAmbientColor()
{
return m_ambientColor;
}
XMFLOAT4 LightClass::GetDiffuseColor()
{
return m_diffuseColor;
}
XMFLOAT3 LightClass::GetDirection()
{
return m_direction;
}
XMFLOAT3 LightClass::GetPosition()
{
return m_position;
}
The view matrix for the light is built using the up vector, the lookAt vector, and the position of the light.
void LightClass::GenerateViewMatrix()
{
XMFLOAT3 up;
XMVECTOR positionVector, lookAtVector, upVector;
// Setup the vector that points upwards.
up.x = 0.0f;
up.y = 1.0f;
up.z = 0.0f;
// Load the XMFLOAT3 into XMVECTOR.
positionVector = XMLoadFloat3(&m_position);
lookAtVector = XMLoadFloat3(&m_lookAt);
upVector = XMLoadFloat3(&up);
// Create the view matrix from the three vectors.
m_viewMatrix = XMMatrixLookAtLH(positionVector, lookAtVector, upVector);
return;
}
The projection matrix for the light is built using the field of view, viewing aspect ratio, and the near and far plane of the light range.
The light we are projecting is more of a square spotlight than a true point light, but this is necessary since we need to align with the sampling from a square shadow map texture.
That is why the field of view and aspect ratio are setup for a square projection.
void LightClass::GenerateProjectionMatrix(float screenDepth, float screenNear)
{
float fieldOfView, screenAspect;
// Setup field of view and screen aspect for a square light source.
fieldOfView = 3.14159265358979323846f / 2.0f;
screenAspect = 1.0f;
// Create the projection matrix for the light.
m_projectionMatrix = XMMatrixPerspectiveFovLH(fieldOfView, screenAspect, screenNear, screenDepth);
return;
}
We also have two new functions to return the view and projection matrices.
void LightClass::GetViewMatrix(XMMATRIX& viewMatrix)
{
viewMatrix = m_viewMatrix;
return;
}
void LightClass::GetProjectionMatrix(XMMATRIX& projectionMatrix)
{
projectionMatrix = m_projectionMatrix;
return;
}
Applicationclass.h
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: applicationclass.h
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#ifndef _APPLICATIONCLASS_H_
#define _APPLICATIONCLASS_H_
/////////////
// GLOBALS //
/////////////
const bool FULL_SCREEN = false;
const bool VSYNC_ENABLED = true;
The screen depth and near have been changed to encapsulate just the scene so we can have maximum amount of float point precision available.
We also added a new define for the shadow map size so it can be easily tweaked.
const float SCREEN_DEPTH = 100.0f;
const float SCREEN_NEAR = 1.0f;
const int SHADOWMAP_WIDTH = 1024;
const int SHADOWMAP_HEIGHT = 1024;
///////////////////////
// MY CLASS INCLUDES //
///////////////////////
#include "d3dclass.h"
#include "inputclass.h"
#include "cameraclass.h"
#include "modelclass.h"
#include "lightclass.h"
We have included headers for the render to texture, depth shader, and shadow shader classes.
#include "rendertextureclass.h"
#include "depthshaderclass.h"
#include "shadowshaderclass.h"
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Class name: ApplicationClass
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class ApplicationClass
{
public:
ApplicationClass();
ApplicationClass(const ApplicationClass&);
~ApplicationClass();
bool Initialize(int, int, HWND);
void Shutdown();
bool Frame(InputClass*);
private:
We will require a function to render the depth of our scene from the light perspective each frame.
This is what creates the shadow map that we then use in our shadow shader.
bool RenderDepthToTexture();
bool Render();
private:
D3DClass* m_Direct3D;
CameraClass* m_Camera;
We have three models for the scene. A cube, a sphere, and a ground plane.
ModelClass *m_CubeModel, *m_SphereModel, *m_GroundModel;
LightClass* m_Light;
We define the render texture, depth shader, and shadow shader objects here.
RenderTextureClass* m_RenderTexture;
DepthShaderClass* m_DepthShader;
ShadowShaderClass* m_ShadowShader;
We also add a variable for easy changing of the shadow map bias which gets sent into the pixel shader each frame.
float m_shadowMapBias;
};
#endif
Applicationclass.cpp
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: applicationclass.cpp
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#include "applicationclass.h"
ApplicationClass::ApplicationClass()
{
m_Direct3D = 0;
m_Camera = 0;
m_CubeModel = 0;
m_SphereModel = 0;
m_GroundModel = 0;
m_Light = 0;
m_RenderTexture = 0;
m_DepthShader = 0;
m_ShadowShader = 0;
}
ApplicationClass::ApplicationClass(const ApplicationClass& other)
{
}
ApplicationClass::~ApplicationClass()
{
}
bool ApplicationClass::Initialize(int screenWidth, int screenHeight, HWND hwnd)
{
char modelFilename[128], textureFilename[128];
bool result;
// Create and initialize the Direct3D object.
m_Direct3D = new D3DClass;
result = m_Direct3D->Initialize(screenWidth, screenHeight, VSYNC_ENABLED, hwnd, FULL_SCREEN, SCREEN_DEPTH, SCREEN_NEAR);
if(!result)
{
MessageBox(hwnd, L"Could not initialize Direct3D.", L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
// Create and initialize the camera object.
m_Camera = new CameraClass;
m_Camera->SetPosition(0.0f, 7.0f, -10.0f);
m_Camera->SetRotation(35.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
m_Camera->Render();
We load a cube model, and sphere model, and a flat plane ground model.
// Create and initialize the cube model object.
m_CubeModel = new ModelClass;
strcpy_s(modelFilename, "../Engine/data/cube.txt");
strcpy_s(textureFilename, "../Engine/data/wall01.tga");
result = m_CubeModel->Initialize(m_Direct3D->GetDevice(), m_Direct3D->GetDeviceContext(), modelFilename, textureFilename);
if(!result)
{
MessageBox(hwnd, L"Could not initialize the cube model object.", L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
// Create and initialize the sphere model object.
m_SphereModel = new ModelClass;
strcpy_s(modelFilename, "../Engine/data/sphere.txt");
strcpy_s(textureFilename, "../Engine/data/ice.tga");
result = m_SphereModel->Initialize(m_Direct3D->GetDevice(), m_Direct3D->GetDeviceContext(), modelFilename, textureFilename);
if(!result)
{
MessageBox(hwnd, L"Could not initialize the sphere model object.", L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
// Create and initialize the ground model object.
m_GroundModel = new ModelClass;
strcpy_s(modelFilename, "../Engine/data/plane01.txt");
strcpy_s(textureFilename, "../Engine/data/metal001.tga");
result = m_GroundModel->Initialize(m_Direct3D->GetDevice(), m_Direct3D->GetDeviceContext(), modelFilename, textureFilename);
if(!result)
{
MessageBox(hwnd, L"Could not initialize the ground model object.", L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
Create our light and set its lookAt to the center of the scene.
Then generate its projection matrix after the lookAt is set using the screen depth and near values.
// Create and initialize the light object.
m_Light = new LightClass;
m_Light->SetAmbientColor(0.15f, 0.15f, 0.15f, 1.0f);
m_Light->SetDiffuseColor(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
m_Light->SetLookAt(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
m_Light->GenerateProjectionMatrix(SCREEN_DEPTH, SCREEN_NEAR);
We create a render to texture object that will be used as the shadow map.
The depth buffer of the scene will be rendered from the light's perspective onto this render to texture object.
We use the shadow map dimensions for sizing the render texture to reflect how the light would view the scene.
// Create and initialize the render to texture object.
m_RenderTexture = new RenderTextureClass;
result = m_RenderTexture->Initialize(m_Direct3D->GetDevice(), SHADOWMAP_WIDTH, SHADOWMAP_HEIGHT, SCREEN_DEPTH, SCREEN_NEAR, 1);
if(!result)
{
MessageBox(hwnd, L"Could not initialize the render texture object.", L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
The depth shader object is created and initialized here.
// Create and initialize the depth shader object.
m_DepthShader = new DepthShaderClass;
result = m_DepthShader->Initialize(m_Direct3D->GetDevice(), hwnd);
if(!result)
{
MessageBox(hwnd, L"Could not initialize the depth shader object.", L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
The shadow shader object is created and initialized here.
// Create and initialize the shadow shader object.
m_ShadowShader = new ShadowShaderClass;
result = m_ShadowShader->Initialize(m_Direct3D->GetDevice(), hwnd);
if(!result)
{
MessageBox(hwnd, L"Could not initialize the shadow shader object.", L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
We will set the shadow map bias here.
This is a crucial setting for the shadow map!
It has to be just the right value or the shadows will not be in the correct location, or will have strange artifacts due to floating point precision issues.
Different sized scenes sometimes require this to be set to different values.
// Set the shadow map bias to fix the floating point precision issues (shadow acne/lines artifacts).
m_shadowMapBias = 0.0022f;
return true;
}
void ApplicationClass::Shutdown()
{
// Release the shadow shader object.
if(m_ShadowShader)
{
m_ShadowShader->Shutdown();
delete m_ShadowShader;
m_ShadowShader = 0;
}
// Release the depth shader object.
if(m_DepthShader)
{
m_DepthShader->Shutdown();
delete m_DepthShader;
m_DepthShader = 0;
}
// Release the render texture object.
if(m_RenderTexture)
{
m_RenderTexture->Shutdown();
delete m_RenderTexture;
m_RenderTexture = 0;
}
// Release the light object.
if(m_Light)
{
delete m_Light;
m_Light = 0;
}
// Release the ground model object.
if(m_GroundModel)
{
m_GroundModel->Shutdown();
delete m_GroundModel;
m_GroundModel = 0;
}
// Release the sphere model object.
if(m_SphereModel)
{
m_SphereModel->Shutdown();
delete m_SphereModel;
m_SphereModel = 0;
}
// Release the cube model object.
if(m_CubeModel)
{
m_CubeModel->Shutdown();
delete m_CubeModel;
m_CubeModel = 0;
}
// Release the camera object.
if(m_Camera)
{
delete m_Camera;
m_Camera = 0;
}
// Release the Direct3D object.
if(m_Direct3D)
{
m_Direct3D->Shutdown();
delete m_Direct3D;
m_Direct3D = 0;
}
return;
}
bool ApplicationClass::Frame(InputClass* Input)
{
static float lightPositionX = -5.0f;
bool result;
// Check if the user pressed escape and wants to exit the application.
if(Input->IsEscapePressed())
{
return false;
}
During the frame we move the light from left to right to see the shadows move in accordance with the light's position.
After the light has moved then update its view matrix.
// Update the position of the light each frame.
lightPositionX += 0.05f;
if(lightPositionX > 5.0f)
{
lightPositionX = -5.0f;
}
// Set the updated position of the light and generate it's new view matrix.
m_Light->SetPosition(lightPositionX, 8.0f, -5.0f);
m_Light->GenerateViewMatrix();
Render the shadow map first.
// Render the scene depth to the render texture.
result = RenderDepthToTexture();
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
Now render the regular scene with shadows using the shadow map.
// Render the graphics scene.
result = Render();
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
The RenderDepthToTexture function is called at the beginning of the frame rendering.
We render the depth buffer of the scene from the perspective of the light into the render to texture object which then becomes our shadow map.
bool ApplicationClass::RenderDepthToTexture()
{
XMMATRIX translateMatrix, lightViewMatrix, lightProjectionMatrix;
bool result;
Set the render to texture to be the rendering target.
// Set the render target to be the render to texture. Also clear the render to texture.
m_RenderTexture->SetRenderTarget(m_Direct3D->GetDeviceContext());
m_RenderTexture->ClearRenderTarget(m_Direct3D->GetDeviceContext(), 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
Use the light's matrices for rendering.
// Get the view and orthographic matrices from the light object.
m_Light->GetViewMatrix(lightViewMatrix);
m_Light->GetProjectionMatrix(lightProjectionMatrix);
Render all the objects in the scene using the depth shader and the light view and projection matrices.
// Setup the translation matrix for the cube model.
translateMatrix = XMMatrixTranslation(-2.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f);
// Render the cube model using the depth shader.
m_CubeModel->Render(m_Direct3D->GetDeviceContext());
result = m_DepthShader->Render(m_Direct3D->GetDeviceContext(), m_CubeModel->GetIndexCount(), translateMatrix, lightViewMatrix, lightProjectionMatrix);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
// Setup the translation matrix for the sphere model.
translateMatrix = XMMatrixTranslation(2.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f);
// Render the sphere model using the depth shader.
m_SphereModel->Render(m_Direct3D->GetDeviceContext());
result = m_DepthShader->Render(m_Direct3D->GetDeviceContext(), m_SphereModel->GetIndexCount(), translateMatrix, lightViewMatrix, lightProjectionMatrix);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
// Setup the translation matrix for the ground model.
translateMatrix = XMMatrixTranslation(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
// Render the ground model using the depth shader.
m_GroundModel->Render(m_Direct3D->GetDeviceContext());
result = m_DepthShader->Render(m_Direct3D->GetDeviceContext(), m_GroundModel->GetIndexCount(), translateMatrix, lightViewMatrix, lightProjectionMatrix);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
Set the rendering target back to normal.
// Reset the render target back to the original back buffer and not the render to texture anymore. Also reset the viewport back to the original.
m_Direct3D->SetBackBufferRenderTarget();
m_Direct3D->ResetViewport();
return true;
}
bool ApplicationClass::Render()
{
XMMATRIX worldMatrix, viewMatrix, projectionMatrix, lightViewMatrix, lightProjectionMatrix;
bool result;
// Clear the buffers to begin the scene.
m_Direct3D->BeginScene(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
// Get the world, view, and projection matrices from the camera and d3d objects.
m_Direct3D->GetWorldMatrix(worldMatrix);
m_Camera->GetViewMatrix(viewMatrix);
m_Direct3D->GetProjectionMatrix(projectionMatrix);
Get the light matrices and lighting properties for rendering the objects with shadows.
// Get the view and projection matrices from the view point object.
m_Light->GetViewMatrix(lightViewMatrix);
m_Light->GetProjectionMatrix(lightProjectionMatrix);
Render the cube using the shadow map shader.
// Setup the translation matrix for the cube model.
worldMatrix = XMMatrixTranslation(-2.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f);
// Render the cube model using the shadow shader.
m_CubeModel->Render(m_Direct3D->GetDeviceContext());
result = m_ShadowShader->Render(m_Direct3D->GetDeviceContext(), m_CubeModel->GetIndexCount(), worldMatrix, viewMatrix, projectionMatrix, lightViewMatrix, lightProjectionMatrix,
m_CubeModel->GetTexture(), m_RenderTexture->GetShaderResourceView(), m_Light->GetAmbientColor(), m_Light->GetDiffuseColor(), m_Light->GetPosition(), m_shadowMapBias);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
Render the sphere using the shadow map shader.
// Setup the translation matrix for the sphere model.
worldMatrix = XMMatrixTranslation(2.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f);
// Render the sphere model using the shadow shader.
m_SphereModel->Render(m_Direct3D->GetDeviceContext());
result = m_ShadowShader->Render(m_Direct3D->GetDeviceContext(), m_SphereModel->GetIndexCount(), worldMatrix, viewMatrix, projectionMatrix, lightViewMatrix, lightProjectionMatrix,
m_SphereModel->GetTexture(), m_RenderTexture->GetShaderResourceView(), m_Light->GetAmbientColor(), m_Light->GetDiffuseColor(), m_Light->GetPosition(), m_shadowMapBias);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
Render the ground using the shadow map shader.
// Setup the translation matrix for the ground model.
worldMatrix = XMMatrixTranslation(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
// Render the ground model using the shadow shader.
m_GroundModel->Render(m_Direct3D->GetDeviceContext());
result = m_ShadowShader->Render(m_Direct3D->GetDeviceContext(), m_GroundModel->GetIndexCount(), worldMatrix, viewMatrix, projectionMatrix, lightViewMatrix, lightProjectionMatrix,
m_GroundModel->GetTexture(), m_RenderTexture->GetShaderResourceView(), m_Light->GetAmbientColor(), m_Light->GetDiffuseColor(), m_Light->GetPosition(), m_shadowMapBias);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
// Present the rendered scene to the screen.
m_Direct3D->EndScene();
return true;
}
Summary
We can now add shadows to any of our scenes using a render to texture of the depth information from the light's perspective.
The variable inputs and same checks can be used with any other shader program to add shadows.
To Do Exercises
1. Recompile the code and run the program and examine the shadows. Press escape to quit.
2. Set the bias to 0.0f in the pixel shader to see the effect when no bias is set.
3. Set the shadow map bias to different values to see how it moves the shadows away from their expected position.
4. Set the SHADOWMAP_WIDTH and SHADOWMAP_HEIGHT to different values (such as 256) to see the effect different resolution shadow maps produce.
5. Move the sphere closer to the cube to see that they shadow each other.
Source Code
Source Code and Data Files: dx11win10tut41_src.zip
![]()
![]()