Texture translation is the technique used to animate a texture moving over a polygon surface.
This tutorial will cover how to implement texture translation using OpenGL 4.0 and GLSL.
The code in this tutorial is based on the previous tutorials.
As discussed in the texturing tutorial we use UV coordinates to map textures to polygons.
The UV coordinates translate to X and Y coordinates with X going horizontally across the polygon face and Y going vertically across the polygon face.
To implement texture translation, we have to modify the X and Y coordinate of the texture in the pixel shader.
We can do this by simply adding or subtracting a value between 0 and 1 to either the X or Y coordinate.
For example, we have the following texture mapped to the polygon:

We then add 0.5 to the texture X coordinate in the pixel shader and it translates the texture coordinates over by half:


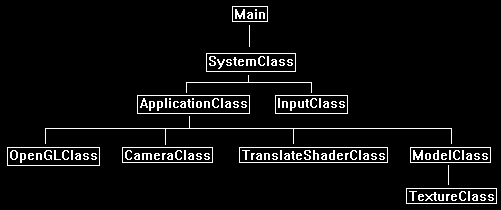
Framework
The frame work has been updated to include the new TranslateShaderClass.
Translate.vs
The vertex shader is the same as the texture vertex shader.
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: translate.vs
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#version 400
/////////////////////
// INPUT VARIABLES //
/////////////////////
in vec3 inputPosition;
in vec2 inputTexCoord;
//////////////////////
// OUTPUT VARIABLES //
//////////////////////
out vec2 texCoord;
///////////////////////
// UNIFORM VARIABLES //
///////////////////////
uniform mat4 worldMatrix;
uniform mat4 viewMatrix;
uniform mat4 projectionMatrix;
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Vertex Shader
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void main(void)
{
// Calculate the position of the vertex against the world, view, and projection matrices.
gl_Position = vec4(inputPosition, 1.0f) * worldMatrix;
gl_Position = gl_Position * viewMatrix;
gl_Position = gl_Position * projectionMatrix;
// Store the texture coordinates for the pixel shader.
texCoord = inputTexCoord;
}
Translate.ps
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: translate.ps
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#version 400
/////////////////////
// INPUT VARIABLES //
/////////////////////
in vec2 texCoord;
//////////////////////
// OUTPUT VARIABLES //
//////////////////////
out vec4 outputColor;
///////////////////////
// UNIFORM VARIABLES //
///////////////////////
uniform sampler2D shaderTexture;
We add a new uniform float variable called textureTranslation.
This is set in the applicationclass.cpp during the Frame function to update the position of the texture translation.
The value set here will be between 0 and 1.
uniform float textureTranslation;
The pixel shader is where we do the work of translating the texture coordinate by the textureTranslation amount.
We take a copy of the input texture coordinate, and then add the translation amount for each pixel shader call.
So now when we sample the texture with these updated coordinates it will uniformly translate the texture across the polygon face.
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Pixel Shader
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void main(void)
{
vec4 textureColor;
vec2 tex;
// Copy the texture coordinates from a read only variable into a variable we can modify.
tex.x = texCoord.x;
tex.y = texCoord.y;
// Translate the position where we sample the pixel from.
tex.x += textureTranslation;
// Sample the pixel color from the texture using the sampler at this texture coordinate location.
textureColor = texture(shaderTexture, tex);
outputColor = textureColor;
}
Translateshaderclass.h
The TranslateShaderClass is just the TextureShaderClass with extra functionality for texture translation.
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: translateshaderclass.h
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#ifndef _TRANSLATESHADERCLASS_H_
#define _TRANSLATESHADERCLASS_H_
//////////////
// INCLUDES //
//////////////
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
///////////////////////
// MY CLASS INCLUDES //
///////////////////////
#include "openglclass.h"
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Class name: TranslateShaderClass
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class TranslateShaderClass
{
public:
TranslateShaderClass();
TranslateShaderClass(const TranslateShaderClass&);
~TranslateShaderClass();
bool Initialize(OpenGLClass*);
void Shutdown();
bool SetShaderParameters(float*, float*, float*, float);
private:
bool InitializeShader(char*, char*);
void ShutdownShader();
char* LoadShaderSourceFile(char*);
void OutputShaderErrorMessage(unsigned int, char*);
void OutputLinkerErrorMessage(unsigned int);
private:
OpenGLClass* m_OpenGLPtr;
unsigned int m_vertexShader;
unsigned int m_fragmentShader;
unsigned int m_shaderProgram;
};
#endif
Translateshaderclass.cpp
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: translateshaderclass.cpp
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#include "translateshaderclass.h"
TranslateShaderClass::TranslateShaderClass()
{
m_OpenGLPtr = 0;
}
TranslateShaderClass::TranslateShaderClass(const TranslateShaderClass& other)
{
}
TranslateShaderClass::~TranslateShaderClass()
{
}
bool TranslateShaderClass::Initialize(OpenGLClass* OpenGL)
{
char vsFilename[128];
char psFilename[128];
bool result;
// Store the pointer to the OpenGL object.
m_OpenGLPtr = OpenGL;
We load the translate.vs and translate.ps GLSL shader files here.
// Set the location and names of the shader files.
strcpy(vsFilename, "../Engine/translate.vs");
strcpy(psFilename, "../Engine/translate.ps");
// Initialize the vertex and pixel shaders.
result = InitializeShader(vsFilename, psFilename);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
void TranslateShaderClass::Shutdown()
{
// Shutdown the shader.
ShutdownShader();
// Release the pointer to the OpenGL object.
m_OpenGLPtr = 0;
return;
}
bool TranslateShaderClass::InitializeShader(char* vsFilename, char* fsFilename)
{
const char* vertexShaderBuffer;
const char* fragmentShaderBuffer;
int status;
// Load the vertex shader source file into a text buffer.
vertexShaderBuffer = LoadShaderSourceFile(vsFilename);
if(!vertexShaderBuffer)
{
return false;
}
// Load the fragment shader source file into a text buffer.
fragmentShaderBuffer = LoadShaderSourceFile(fsFilename);
if(!fragmentShaderBuffer)
{
return false;
}
// Create a vertex and fragment shader object.
m_vertexShader = m_OpenGLPtr->glCreateShader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER);
m_fragmentShader = m_OpenGLPtr->glCreateShader(GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER);
// Copy the shader source code strings into the vertex and fragment shader objects.
m_OpenGLPtr->glShaderSource(m_vertexShader, 1, &vertexShaderBuffer, NULL);
m_OpenGLPtr->glShaderSource(m_fragmentShader, 1, &fragmentShaderBuffer, NULL);
// Release the vertex and fragment shader buffers.
delete [] vertexShaderBuffer;
vertexShaderBuffer = 0;
delete [] fragmentShaderBuffer;
fragmentShaderBuffer = 0;
// Compile the shaders.
m_OpenGLPtr->glCompileShader(m_vertexShader);
m_OpenGLPtr->glCompileShader(m_fragmentShader);
// Check to see if the vertex shader compiled successfully.
m_OpenGLPtr->glGetShaderiv(m_vertexShader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &status);
if(status != 1)
{
// If it did not compile then write the syntax error message out to a text file for review.
OutputShaderErrorMessage(m_vertexShader, vsFilename);
return false;
}
// Check to see if the fragment shader compiled successfully.
m_OpenGLPtr->glGetShaderiv(m_fragmentShader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &status);
if(status != 1)
{
// If it did not compile then write the syntax error message out to a text file for review.
OutputShaderErrorMessage(m_fragmentShader, fsFilename);
return false;
}
// Create a shader program object.
m_shaderProgram = m_OpenGLPtr->glCreateProgram();
// Attach the vertex and fragment shader to the program object.
m_OpenGLPtr->glAttachShader(m_shaderProgram, m_vertexShader);
m_OpenGLPtr->glAttachShader(m_shaderProgram, m_fragmentShader);
// Bind the shader input variables.
m_OpenGLPtr->glBindAttribLocation(m_shaderProgram, 0, "inputPosition");
m_OpenGLPtr->glBindAttribLocation(m_shaderProgram, 1, "inputTexCoord");
// Link the shader program.
m_OpenGLPtr->glLinkProgram(m_shaderProgram);
// Check the status of the link.
m_OpenGLPtr->glGetProgramiv(m_shaderProgram, GL_LINK_STATUS, &status);
if(status != 1)
{
// If it did not link then write the syntax error message out to a text file for review.
OutputLinkerErrorMessage(m_shaderProgram);
return false;
}
return true;
}
void TranslateShaderClass::ShutdownShader()
{
// Detach the vertex and fragment shaders from the program.
m_OpenGLPtr->glDetachShader(m_shaderProgram, m_vertexShader);
m_OpenGLPtr->glDetachShader(m_shaderProgram, m_fragmentShader);
// Delete the vertex and fragment shaders.
m_OpenGLPtr->glDeleteShader(m_vertexShader);
m_OpenGLPtr->glDeleteShader(m_fragmentShader);
// Delete the shader program.
m_OpenGLPtr->glDeleteProgram(m_shaderProgram);
return;
}
char* TranslateShaderClass::LoadShaderSourceFile(char* filename)
{
FILE* filePtr;
char* buffer;
long fileSize, count;
int error;
// Open the shader file for reading in text modee.
filePtr = fopen(filename, "r");
if(filePtr == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
// Go to the end of the file and get the size of the file.
fseek(filePtr, 0, SEEK_END);
fileSize = ftell(filePtr);
// Initialize the buffer to read the shader source file into, adding 1 for an extra null terminator.
buffer = new char[fileSize + 1];
// Return the file pointer back to the beginning of the file.
fseek(filePtr, 0, SEEK_SET);
// Read the shader text file into the buffer.
count = fread(buffer, 1, fileSize, filePtr);
if(count != fileSize)
{
return 0;
}
// Close the file.
error = fclose(filePtr);
if(error != 0)
{
return 0;
}
// Null terminate the buffer.
buffer[fileSize] = '\0';
return buffer;
}
void TranslateShaderClass::OutputShaderErrorMessage(unsigned int shaderId, char* shaderFilename)
{
long count;
int logSize, error;
char* infoLog;
FILE* filePtr;
// Get the size of the string containing the information log for the failed shader compilation message.
m_OpenGLPtr->glGetShaderiv(shaderId, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &logSize);
// Increment the size by one to handle also the null terminator.
logSize++;
// Create a char buffer to hold the info log.
infoLog = new char[logSize];
// Now retrieve the info log.
m_OpenGLPtr->glGetShaderInfoLog(shaderId, logSize, NULL, infoLog);
// Open a text file to write the error message to.
filePtr = fopen("shader-error.txt", "w");
if(filePtr == NULL)
{
cout << "Error opening shader error message output file." << endl;
return;
}
// Write out the error message.
count = fwrite(infoLog, sizeof(char), logSize, filePtr);
if(count != logSize)
{
cout << "Error writing shader error message output file." << endl;
return;
}
// Close the file.
error = fclose(filePtr);
if(error != 0)
{
cout << "Error closing shader error message output file." << endl;
return;
}
// Notify the user to check the text file for compile errors.
cout << "Error compiling shader. Check shader-error.txt for error message. Shader filename: " << shaderFilename << endl;
return;
}
void TranslateShaderClass::OutputLinkerErrorMessage(unsigned int programId)
{
long count;
FILE* filePtr;
int logSize, error;
char* infoLog;
// Get the size of the string containing the information log for the failed shader compilation message.
m_OpenGLPtr->glGetProgramiv(programId, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &logSize);
// Increment the size by one to handle also the null terminator.
logSize++;
// Create a char buffer to hold the info log.
infoLog = new char[logSize];
// Now retrieve the info log.
m_OpenGLPtr->glGetProgramInfoLog(programId, logSize, NULL, infoLog);
// Open a file to write the error message to.
filePtr = fopen("linker-error.txt", "w");
if(filePtr == NULL)
{
cout << "Error opening linker error message output file." << endl;
return;
}
// Write out the error message.
count = fwrite(infoLog, sizeof(char), logSize, filePtr);
if(count != logSize)
{
cout << "Error writing linker error message output file." << endl;
return;
}
// Close the file.
error = fclose(filePtr);
if(error != 0)
{
cout << "Error closing linker error message output file." << endl;
return;
}
// Pop a message up on the screen to notify the user to check the text file for linker errors.
cout << "Error linking shader program. Check linker-error.txt for message." << endl;
return;
}
The SetShaderParameters function now takes as input the translation value to be used for translating the texture in the pixel shader.
bool TranslateShaderClass::SetShaderParameters(float* worldMatrix, float* viewMatrix, float* projectionMatrix, float textureTranslation)
{
float tpWorldMatrix[16], tpViewMatrix[16], tpProjectionMatrix[16];
int location;
// Transpose the matrices to prepare them for the shader.
m_OpenGLPtr->MatrixTranspose(tpWorldMatrix, worldMatrix);
m_OpenGLPtr->MatrixTranspose(tpViewMatrix, viewMatrix);
m_OpenGLPtr->MatrixTranspose(tpProjectionMatrix, projectionMatrix);
// Install the shader program as part of the current rendering state.
m_OpenGLPtr->glUseProgram(m_shaderProgram);
// Set the world matrix in the vertex shader.
location = m_OpenGLPtr->glGetUniformLocation(m_shaderProgram, "worldMatrix");
if(location == -1)
{
cout << "World matrix not set." << endl;
}
m_OpenGLPtr->glUniformMatrix4fv(location, 1, false, tpWorldMatrix);
// Set the view matrix in the vertex shader.
location = m_OpenGLPtr->glGetUniformLocation(m_shaderProgram, "viewMatrix");
if(location == -1)
{
cout << "View matrix not set." << endl;
}
m_OpenGLPtr->glUniformMatrix4fv(location, 1, false, tpViewMatrix);
// Set the projection matrix in the vertex shader.
location = m_OpenGLPtr->glGetUniformLocation(m_shaderProgram, "projectionMatrix");
if(location == -1)
{
cout << "Projection matrix not set." << endl;
}
m_OpenGLPtr->glUniformMatrix4fv(location, 1, false, tpProjectionMatrix);
// Set the texture in the pixel shader to use the data from the first texture unit.
location = m_OpenGLPtr->glGetUniformLocation(m_shaderProgram, "shaderTexture");
if(location == -1)
{
cout << "Shader texture not set." << endl;
}
m_OpenGLPtr->glUniform1i(location, 0);
We set the translation value in the pixel shader here.
// Set the texture translation in the pixel shader.
location = m_OpenGLPtr->glGetUniformLocation(m_shaderProgram, "textureTranslation");
if(location == -1)
{
cout << "Texture translation not set." << endl;
}
m_OpenGLPtr->glUniform1f(location, textureTranslation);
return true;
}
Applicationclass.h
The ApplicationClass has the translateshaderclass.h included and a new TranslateShaderClass variable.
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: applicationclass.h
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#ifndef _APPLICATIONCLASS_H_
#define _APPLICATIONCLASS_H_
/////////////
// GLOBALS //
/////////////
const bool FULL_SCREEN = false;
const bool VSYNC_ENABLED = true;
const float SCREEN_NEAR = 0.3f;
const float SCREEN_DEPTH = 1000.0f;
///////////////////////
// MY CLASS INCLUDES //
///////////////////////
#include "inputclass.h"
#include "openglclass.h"
#include "modelclass.h"
#include "cameraclass.h"
#include "translateshaderclass.h"
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Class Name: ApplicationClass
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class ApplicationClass
{
public:
ApplicationClass();
ApplicationClass(const ApplicationClass&);
~ApplicationClass();
bool Initialize(Display*, Window, int, int);
void Shutdown();
bool Frame(InputClass*);
private:
bool Render(float);
private:
OpenGLClass* m_OpenGL;
ModelClass* m_Model;
CameraClass* m_Camera;
TranslateShaderClass* m_TranslateShader;
};
#endif
Applicationclass.cpp
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: applicationclass.cpp
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#include "applicationclass.h"
ApplicationClass::ApplicationClass()
{
m_OpenGL = 0;
m_Model = 0;
m_Camera = 0;
m_TranslateShader = 0;
}
ApplicationClass::ApplicationClass(const ApplicationClass& other)
{
}
ApplicationClass::~ApplicationClass()
{
}
bool ApplicationClass::Initialize(Display* display, Window win, int screenWidth, int screenHeight)
{
char modelFilename[128];
char textureFilename[128];
bool result;
// Create and initialize the OpenGL object.
m_OpenGL = new OpenGLClass;
result = m_OpenGL->Initialize(display, win, screenWidth, screenHeight, SCREEN_NEAR, SCREEN_DEPTH, VSYNC_ENABLED);
if(!result)
{
cout << "Error: Could not initialize the OpenGL object." << endl;
return false;
}
// Create and initialize the camera object.
m_Camera = new CameraClass;
m_Camera->SetPosition(0.0f, 0.0f, -5.0f);
m_Camera->Render();
We will load the square model since it is the most straight forward for displaying the translate effect.
// Set the file name of the model.
strcpy(modelFilename, "../Engine/data/square.txt");
// Set the file name of the texture.
strcpy(textureFilename, "../Engine/data/stone01.tga");
// Create and initialize the model object.
m_Model = new ModelClass;
Wrap must be set to true when loading the texture for the model so that the texture wraps around evenly to the other side when values are outside the 0 to 1 range.
result = m_Model->Initialize(m_OpenGL, modelFilename, textureFilename, true, NULL, true, NULL, true);
if(!result)
{
cout << "Error: Could not initialize the model object." << endl;
return false;
}
The new TranslateShaderClass object is created here.
// Create and initialize the translate shader object.
m_TranslateShader = new TranslateShaderClass;
result = m_TranslateShader->Initialize(m_OpenGL);
if(!result)
{
cout << "Error: Could not initialize the translate shader object." << endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
void ApplicationClass::Shutdown()
{
The new TranslateShaderClass object is released here during Shutdown.
// Release the translate shader object.
if(m_TranslateShader)
{
m_TranslateShader->Shutdown();
delete m_TranslateShader;
m_TranslateShader = 0;
}
// Release the model object.
if(m_Model)
{
m_Model->Shutdown();
delete m_Model;
m_Model = 0;
}
// Release the camera object.
if(m_Camera)
{
delete m_Camera;
m_Camera = 0;
}
// Release the OpenGL object.
if(m_OpenGL)
{
m_OpenGL->Shutdown();
delete m_OpenGL;
m_OpenGL = 0;
}
return;
}
bool ApplicationClass::Frame(InputClass* Input)
{
static float textureTranslation = 0.0f;
bool result;
// Check if the escape key has been pressed, if so quit.
if(Input->IsEscapePressed() == true)
{
return false;
}
Here the translation value is incremented by a small amount each frame.
If it goes over 1.0 then it is reset down to 0.0 again.
// Increment the texture translation.
textureTranslation += 0.01f;
if(textureTranslation > 1.0f)
{
textureTranslation -= 1.0f;
}
// Render the graphics scene.
result = Render(textureTranslation);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool ApplicationClass::Render(float textureTranslation)
{
float worldMatrix[16], viewMatrix[16], projectionMatrix[16];
bool result;
// Clear the buffers to begin the scene.
m_OpenGL->BeginScene(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
// Get the world, view, and projection matrices from the opengl and camera objects.
m_OpenGL->GetWorldMatrix(worldMatrix);
m_Camera->GetViewMatrix(viewMatrix);
m_OpenGL->GetProjectionMatrix(projectionMatrix);
We set the updated translation value in the TranslateShaderClass object each frame and render the model using the shader.
// Set the translate shader as the current shader program and set the matrices and texture translation that it will use for rendering.
result = m_TranslateShader->SetShaderParameters(worldMatrix, viewMatrix, projectionMatrix, textureTranslation);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
// Render the model.
m_Model->SetTexture1(0);
m_Model->Render();
// Present the rendered scene to the screen.
m_OpenGL->EndScene();
return true;
}
Summary
Using a very simple pixel shader we can achieve a very useful effect.
This can be modified to affect how textures appear on surfaces and we can create a wide variety of effects by doing some simple math with the texture coordinates or by animating different textures over planes to simulation motion.

To Do Exercises
1. Recompile the code and ensure you get a texture translating across the polygon surface.
2. Change the pixel shader to affect the Y axis instead of the X axis.
3. Change the pixel shader to affect both the Y axis and then X axis by the same translation value.
Source Code
Source Code and Data Files: gl4linuxtut28_src.tar.gz
![]()
![]()